Analyzing observations of an X-ray flare and becoming the facts with theoretical models, University of Arizona astronomers documented a deadly stumble upon among an unfortunate famous person and an intermediate-mass black hollow.
While black holes and infants don’t appear to have tons in common, they’re remarkably comparable in a single aspect: Both are messy eaters, producing adequate proof that a meal has taken place.
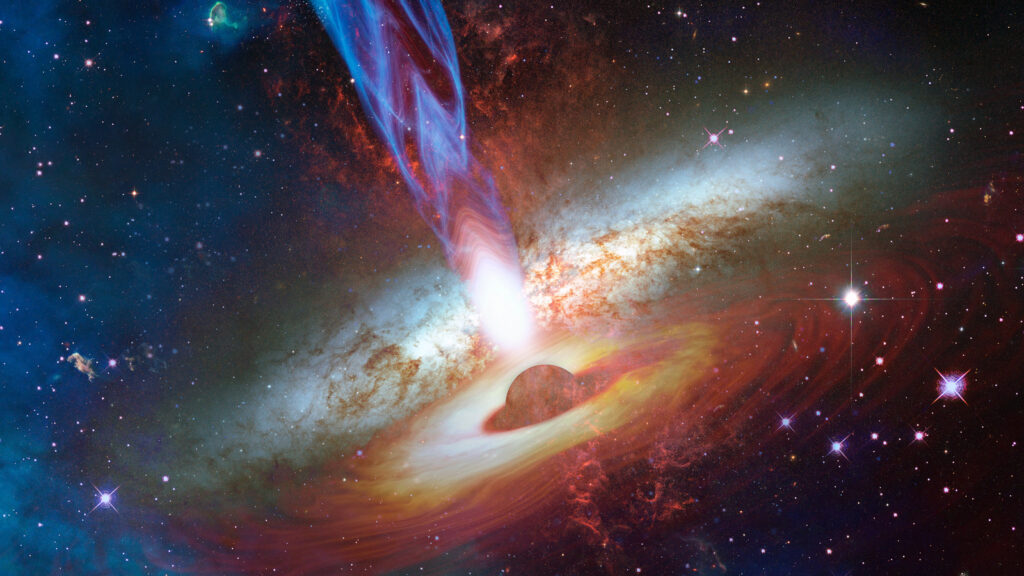
But while one may go away at the back of droppings of pasta or splatters of yogurt, the opposite creates an aftermath of mind-boggling proportions. When a black hollow gobbles up a celebrity, it produces what astronomers name a “tidal disruption occasion.” The shredding of the hapless famous person is observed with the aid of using an outburst of radiation that may outshine the blended mild of each famous person withinside the black hollow’s host galaxy for months, even years.
In a paper posted in The Astrophysical Journal, a group of astronomers led with the aid of using Sixiang Wen, a postdoctoral studies accomplice on the University of Arizona Steward Observatory, use the X-rays emitted with the aid of using a tidal disruption occasion called J2150 to make the primary measurements of each the black hollow’s mass and spin. This black hollow is of a selected type – an intermediate-mass black hollow – which has lengthy eluded observation.
“The reality that we had been capable of capture this black hollow even as it turned into devouring a celebrity gives a amazing possibility to examine what in any other case might be invisible,” stated Ann Zabludoff, UArizona professor of astronomy and co-creator at the paper. “Not handiest that, with the aid of using studying the flare we had been capable of higher apprehend this elusive class of black holes, which might also additionally properly account for almost all of black holes withinside the facilities of galaxies.”
By re-studying the X-ray facts used to examine the J2150 flare, and evaluating it with state-of-the-art theoretical models, the authors confirmed that this flare did certainly originate from an stumble upon among an unfortunate famous person and an intermediate-mass black hollow. The intermediate black hollow in query is of in particular low mass – for a black hollow, that is – weighing in at more or less 10,000 instances the mass of the sun.
“The X-ray emissions from the internal disk shaped with the aid of using the particles of the useless famous person made it viable for us to deduce the mass and spin of this black hollow and classify it as an intermediate black hollow,” Wen stated.
Dozens of tidal disruption occasions were visible withinside the facilities of big galaxies web website hosting supermassive black holes, and a handful have additionally been determined withinside the facilities of small galaxies that could comprise intermediate black holes. However, beyond facts has by no means been distinctive sufficient to show that an person tidal disruption flare turned into powered with the aid of using an intermediate black hollow.
“Thanks to trendy astronomical observations, we recognize that the facilities of virtually all galaxies which can be just like or large in length than our Milky Way host imperative supermassive black holes,” stated take a look at co-creator Nicholas Stone, a senior lecturer at Hebrew University in Jerusalem. “These behemoths variety in length from 1 million to ten billion instances the mass of our sun, and that they emerge as effective reassets of electromagnetic radiation whilst an excessive amount of interstellar fueloline falls into their vicinity.”
The mass of those black holes correlates carefully with the overall mass in their host galaxies; the biggest galaxies host the biggest supermassive black holes.
“We nevertheless recognize little or no approximately the life of black holes withinside the facilities of galaxies smaller than the Milky Way,” stated co-creator Peter Jonker of Radboud University and SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research, each withinside the Netherlands. “Due to observational limitations, it’s miles tough to find out imperative black holes tons smaller than 1 million sun loads.”
Despite their presumed abundance, the origins of supermassive black holes continue to be unknown, and plenty of exceptional theories presently vie to provide an explanation for them, in step with Jonker. Intermediate-mass black holes may be the seeds from which supermassive black holes grow.
“Therefore, if we get a higher manage of what number of bona fide intermediate black holes are out there, it is able to assist decide which theories of supermassive black hollow formation are correct,” he stated.
Even greater exciting, in step with Zabludoff, is the dimension of J2150’s spin that the organization turned into capable of obtain. The spin dimension holds clues as to how black holes grow, and likely to particle physics.
This black hollow has a quick spin, however now no longer the quickest viable spin, Zabludoff explained, begging the query of ways the black hollow finally ends up with a spin on this variety.
“It’s viable that the black hollow shaped that manner and hasn’t modified tons since, or that intermediate-mass black holes merged currently to shape this one,” she stated. “We do recognize that the spin we measured excludes situations in which the black hollow grows over a long term from gradually ingesting fueloline or from many short fueloline snacks that arrive from random directions.”
In addition, the spin dimension permits astrophysicists to check hypotheses approximately the character of darkish depend, that is concept to make up maximum of the problem withinside the universe. Dark depend might also additionally include unknown standard debris now no longer but visible in laboratory experiments. Among the applicants are hypothetical debris called ultralight bosons, Stone explained.
“If the ones debris exist and feature loads in a sure variety, they’ll save you an intermediate-mass black hollow from having a quick spin,” he stated. “Yet J2150’s black hollow is spinning fast. So, our spin dimension guidelines out a wide magnificence of ultralight boson theories, showcasing the fee of black holes as extraterrestrial laboratories for particle physics.”
In the future, new observations of tidal disruption flares may allow astronomers fill withinside the gaps withinside the black hollow mass distribution, the authors hope.
“If it seems that maximum dwarf galaxies comprise intermediate-mass black holes, then they’ll dominate the price of stellar tidal disruption,” Stone stated. “By becoming the X-ray emission from those flares to theoretical models, we are able to behavior a census of the intermediate-mass black hollow populace withinside the universe,” Wen added.
To do that, however, greater tidal disruption occasions must be determined. That’s why astronomers maintain excessive hopes for brand spanking new telescopes coming on line soon, each on Earth and in space, which includes the Vera C. Rubin Observatory, additionally called the Legacy Survey of Space and Time, or LSST, that is predicted to find out hundreds of tidal disruption occasions according to year.
Reference: “Mass, Spin, and Ultralight Boson Constraints from the Intermediate-mass Black Hole withinside the Tidal Disruption Event 3XMM J215022.4–055108” with the aid of using Sixiang Wen, Peter G. Jonker, Nicholas C. Stone and Ann I. Zabludoff, 6 September 2021, The Astrophysical Journal.
This studies turned into supported with the aid of using presents from NASA and the U.S.-Israel Binational Science Foundation.







More Stories
NASA’s Space Robots Work With Astronauts In International Space Station For The First Time
How Did Earth Become a Habitable Planet?
Why NASA’s Annoyed About Elon Musk’s Giant Rocket